What is the Difference Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protectors
In industrial and commercial power systems, choosing the appropriate overvoltage and undervoltage protectors helps protect equipment and maintain stable operation. Although the working principles of single-phase and three-phase protectors are similar, they differ in structure, applicable scenarios and performance. This article will analyze the differences between these two types of protectors from the perspective of practical application.
Before understanding the differences between these two types of protectors, we need to first grasp the basic concepts of single-phase electricity and three-phase electricity, as well as their connection with overvoltage and undervoltage protectors.
Difference Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Electricity
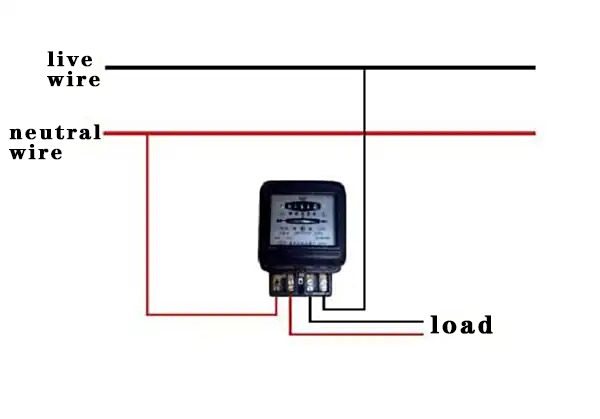
Single-Phase Electricity
- Structure: Consists of one live wire (L) and one neutral wire (N). Sometimes a ground wire is added for safety.
- Voltage: Typically 220V (Asia-Pacific) or 110V (Americas).
- Application Scenarios: Mainly used for lighting, household appliances (such as refrigerators, air conditioners), and small equipment.
- Characteristics: Simple structure, low cost, but relatively poor power supply stability. Suitable for low-power loads.
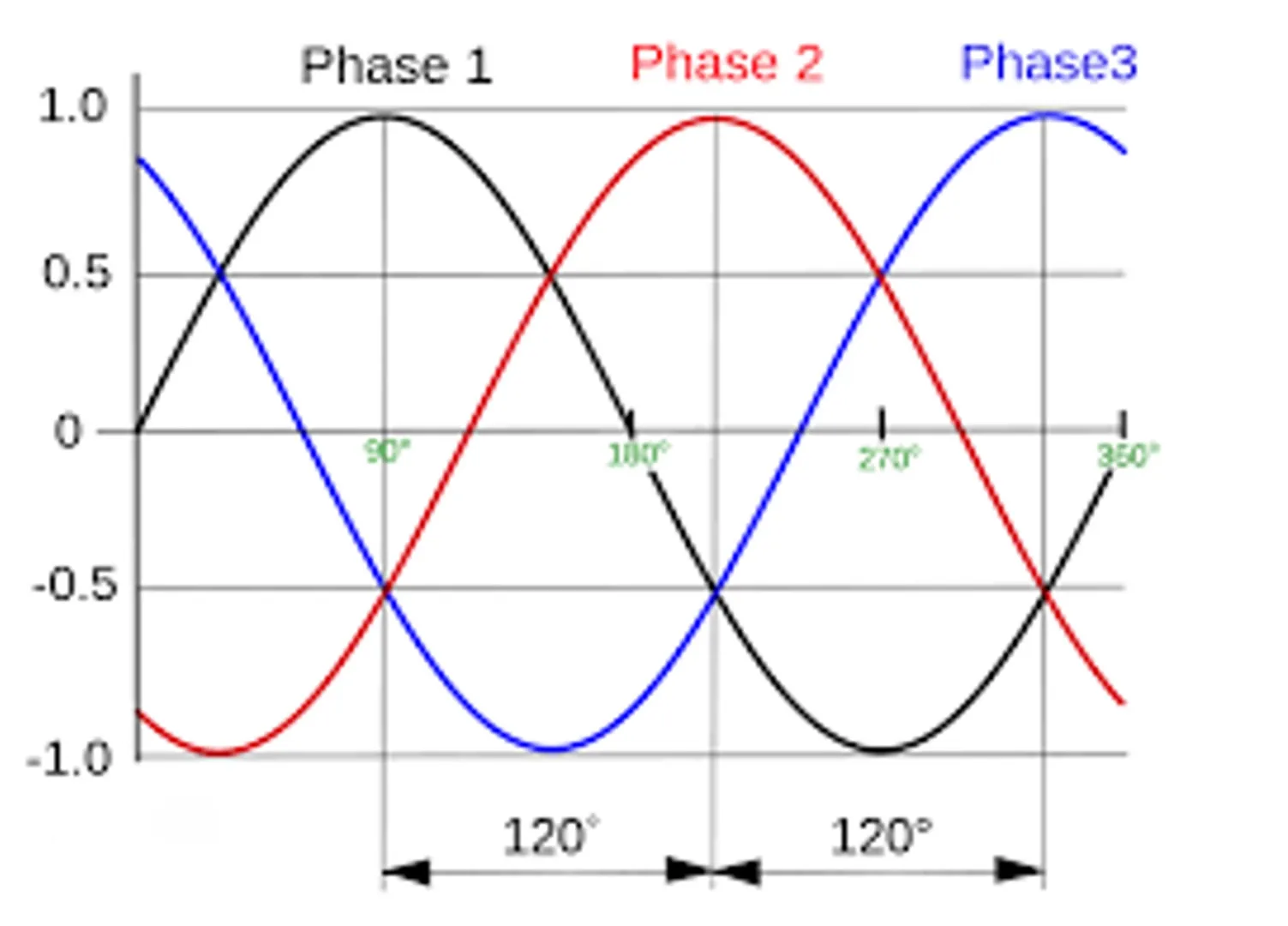
Three-Phase Electricity
- Structure: Consists of three live wires and one neutral wire. Sometimes a ground wire is added.
- Voltage: Typically 380V, suitable for industry, large equipment, and high-power loads.
- Application Scenarios: Used in factories, for large motors, compressors, industrial equipment, etc.
- Characteristics: Stable power supply, high efficiency, capable of carrying higher power. However, the structure is more complex, requiring professional installation and maintenance.
After understanding the basic differences between the two electrical systems, it becomes easier to understand the functional differences between the two types of overvoltage and undervoltage protectors.
Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protectors
Voltage
The main difference between these two types of protectors lies in the voltage systems they are applicable to: single-phase protectors are used in single-phase systems, while three-phase protectors are used in three-phase systems.
Protection
The structure of a single-phase protector is relatively simple. It only needs to monitor single-phase voltage and has a relatively single function, lacking the ability to protect against phase failure. The three-phase protector needs to monitor the three-phase voltage simultaneously, and also detect the phase sequence and phase failure conditions. Therefore, it has the functions of phase loss and phase failure protection, making its functionality more comprehensive.
Wiring
Single-phase protectors are usually available in 1P or 2P configurations. The 1P version only protects the phase line, while the 2P version protects both the phase line and the neutral line, providing more comprehensive protection.
Three-phase protectors are available in 3P or 4P configurations. The 3P version only protects three phase lines, while the 4P version protects all three phases plus the neutral wire. The 4P configuration is usually recommended for full protection, especially in environments where a neutral line failure may cause significant damage.

Conclusion
Both single-phase and three-phase overvoltage and undervoltage protectors are used to protect electrical equipment during voltage abnormalities, but they differ in design principles and applicable scenarios. Single-phase protectors are mostly used in residential or light commercial settings. Their structure is relatively simple, and the cost is lower, making them suitable for general single-phase circuits. Three-phase protectors can monitor multi-phase voltage status and handle phase balance. They are typically used in industrial power systems and are suitable for application in three-phase circuits.
When selecting a protector, it is recommended to comprehensively consider the actual power supply type, load requirements, installation conditions, and potential future expansion needs.
If you need personalized recommendations or guidance on model selection, please feel free to contact us. Get professional support.




